
This lesson discusses about how teachers can adjust in their teaching process as to suit and engage with the new digital learners, in which they should be guided as to what to be developed as the learner are into it. There were also six essential skills to equip students which they call them fluency skills.
First is the solution fluency, which refers to capacity and creativity in problem solving.

Second is the information fluency, which involves 3 submits skills which are the ability to access, retrieve and reflect information.

Third is the collaboration fluency, which refers to teamwork with virtual or real partners in online environment.

Fourth is the media fluency, which refers to channel of mass communication.

Fifth is the creativity fluency, which is artistic proficiency adds meaning by way of design, art and storytelling to package a message.

Lastly is the digital ethics, which was guided by principles of leadership, global responsibility, environmental awareness, global citizenship and personal accountability. Another point is the higher thinking skills.

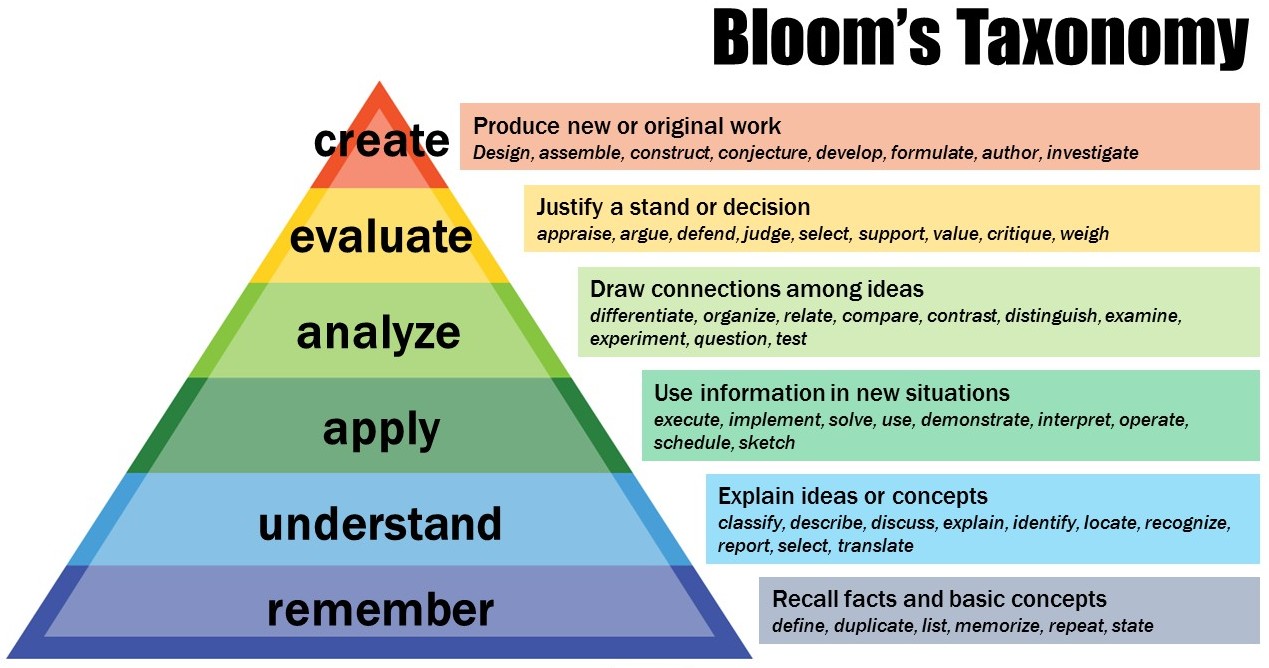
Bloom’s Taxonomy serves as a general framework of skills that requires information processing, idea creation and real-world problem-solving skills. The following taxonomy may be proposed: remembering, understanding, applying, analyzing, evaluating and creating.
First is the solution fluency, which refers to capacity and creativity in problem solving.

Second is the information fluency, which involves 3 submits skills which are the ability to access, retrieve and reflect information.
Third is the collaboration fluency, which refers to teamwork with virtual or real partners in online environment.
Fourth is the media fluency, which refers to channel of mass communication.
Fifth is the creativity fluency, which is artistic proficiency adds meaning by way of design, art and storytelling to package a message.
Lastly is the digital ethics, which was guided by principles of leadership, global responsibility, environmental awareness, global citizenship and personal accountability. Another point is the higher thinking skills.
Bloom’s Taxonomy serves as a general framework of skills that requires information processing, idea creation and real-world problem-solving skills. The following taxonomy may be proposed: remembering, understanding, applying, analyzing, evaluating and creating.

Complex Thinking Skills
|
Sub-Skills
|
Focusing
|
Defining the problem, goal/ objective- setting, brainstorming
|
Information gathering
|
Selection, recording of data of information
|
Remembering
|
Associating, relating new data with old
|
Analysis
|
Identifying idea constructs, patterns
|
Generating
|
Deducing, inducting, elaborating
|
Organizing
|
Classifying, relating
|
Imagining
|
Visualizing, predicting
|
Designing
|
Planning, formulating
|
Integration
|
Summarizing, abstracting
|
Evaluating
|
Setting criteria, testing idea, verifying outcomes, revising
|
We also discussed the structured problem solving-process known as 4D’s that also exemplifies the instructional shift in digital learning: define the problem, design the solution, do the work and debrief on the outcome.
Walang komento:
Mag-post ng isang Komento